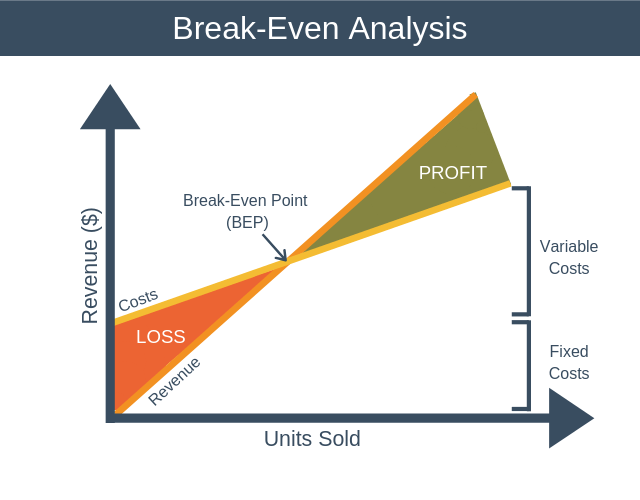
Concept of Break-Even Analysis:
Break-Even
Analysis is a concept used very widely in production management and
cost. It is an analytical tool which helps the firm to identify that
level
of sale where it will cover its cost of production. Any sale over and
above the
break- Even Point will accrue profits to the firm, while any sales less
than it
would put the firm into losses. The Break-Even Point shows the price at
which
the firm makes neither profit nor loss. Break-Even point is a very
significant
concept in Economics and business, especially in Cost Accounting.
Break-Even
point is a point where the cost of production and the revenue from
sales are exactly equal to each other; which means that the firm has neither
made profits nor has incurred any losses. The Break-Even Analysis is also
known as the Cost- Volume- Profit Analysis and is used to study the
relationship between total cost, total revenue, profits and losses. It also
helps to determine that level of output which is required to cover the
operating costs of a business.
Limitations of Break-Even Analysis:
For the break-
even point to be counted, all costs need to be clearly categorized in fixed and
variable costs, which may not be possible every time.
For the multiple-
product or joint- product operations, it is difficult to apply the break-even
analysis. on needs to ascertain the costs to each product, hence the
analysis is applicable only for a single product.
The computation of the break-even point is based on the historical information. If this information
is not relevant, the analysis cannot be applied usefully.
Significance of Break-Even Analysis:
The
break-even
analysis helps us to determine the levels of sales necessary to meet all
the
operating costs. With the estimates of revenue and costs, we can
forecast the
profits. One can also appraise the effects of change in price, fixed
costs and
variable cost on sales volume, total cost and total revenue and in turn,
on the break-even point. One can compare the profit earning capacities
of different
firms. It can also bring out the significance of capacity utilization
for
achieving economy.
Video
Lecture Links:
Comments
Post a Comment